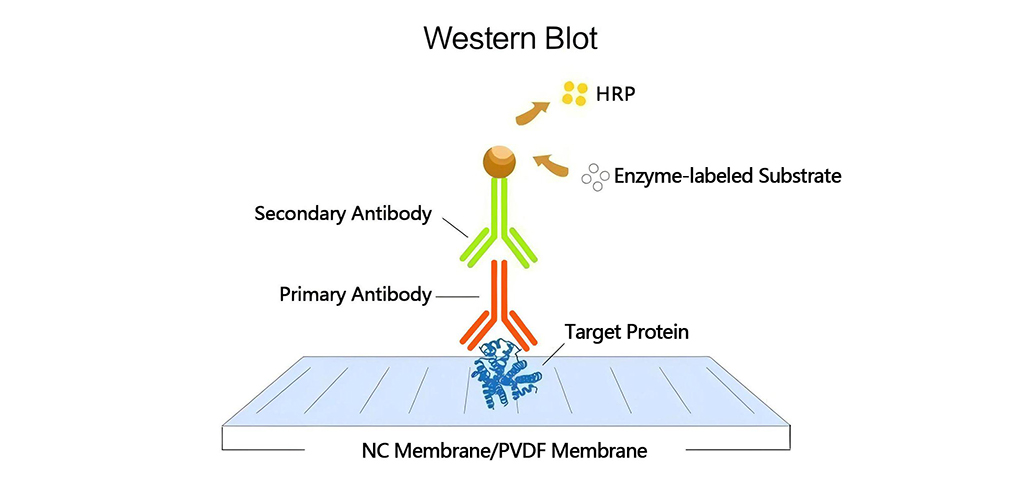
Q1: What is the fundamental principle of Western blotting?
A: Western blotting (WB) is an immunodetection technique that involves:
- Electrophoretic separation of proteins by SDS-PAGE
- Electroblotting transfer to solid-phase membranes (nitrocellulose or PVDF)
- Immunoprobing with target-specific primary antibodies
- Detection using enzyme-conjugated secondary antibodies
The technique provides specific protein identification through antigen-antibody interactions, with applications ranging from protein expression analysis to diagnostic testing.
Q2: Why is methanol pretreatment required for PVDF membranes?
A: PVDF membranes require methanol activation because:
- PVDF is intrinsically hydrophobic (contact angle >100°)
- Methanol (50% v/v) reduces surface tension, enabling aqueous buffer penetration
- Optimal treatment involves:
30 sec immersion for wet transfer
15 sec for semi-dry transfer
Subsequent equilibration in transfer buffer (5 min)
Q3: How to select appropriate membrane pore size?
A: Pore size selection criteria:
Parameter | 0.2 μm PVDF | 0.45 μm PVDF |
Protein size | <20 kDa (90% retention) | >20 kDa |
Binding capacity | ~200 μg/cm² | ~150 μg/cm² |
Resolution | High | Moderate |
Flow resistance | High | Low |
Q4: What are the recommended transfer conditions?
A: Optimal transfer parameters:
- Buffer composition: 25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, 20% methanol
- Current: 200-300 mA (constant)
- Duration: 60-90 min for 10% gels
- Temperature: Maintain at 4°C
- For small proteins (<20 kDa):
- Reduce methanol to 10%
- Decrease transfer time to 30 min
- Use 0.2 μm PVDF membrane
Q5: How to verify transfer efficiency?
A: Recommended verification methods:
- Reversible staining:
- Ponceau S (0.2% in 1% acetic acid)
- Sensitivity: 0.5-1 μg/band
- Compatible with subsequent immunodetection
- Irreversible staining:
- Coomassie Brilliant Blue
- Sensitivity: 0.05 μg/band
- Destructive to membrane
Q6: What are the key differences between PVDF and NC membranes?
A: Comparative analysis:
Characteristic | PVDF Membrane | NC Membrane |
Mechanical strength | 40-60 MPa | 10-15 MPa |
Chemical resistance | pH 1-13 stable | Degrades at pH extremes |
Temperature range | -70°C to 150°C | -20°C to 40°C |
Protein binding | Hydrophobic interaction | Non-covalent adsorption |
Cost | $0.8-1.2/cm² | $0.3-0.5/cm² |
Q7: How to properly store blotted membranes?
A: Recommended storage protocol:
- Sandwich membrane between filter papers
- Place in sealed plastic bag with desiccant
- Storage conditions:
- Short-term: 4°C (≤2 weeks)
- Medium-term: -20°C (≤2 months)
- Long-term: -70°C (years)
Critical note: Never allow membranes to dry if intending for reprobing
Q8: What are the troubleshooting solutions for common WB issues?
A: Technical solutions:
- High background
- Cause: Insufficient blocking
- Solution: Extend blocking time (1 hr with 5% BSA) or use protein-free blockers
- Weak signal
- Cause: Over-diluted antibodies
- Solution: Perform antibody titration (recommended range: 1:500-1:5000)
- Poor transfer efficiency
- Cause: Improper membrane selection
- Solution: For small proteins (<20 kDa):
- Use 0.2 μm PVDF
- Reduce transfer time to 30 min
- Decrease methanol to 10%
- Non-specific bands
- Cause: Antibody cross-reactivity
- Solution: Include control lysates and validate antibodies
Q9: When should PVDF vs NC membranes be selected?
A: Selection guidelines:
Choose PVDF when:
- Detecting small proteins (<20 kDa)
- Operating in harsh conditions (organic solvents, extreme pH)
- Requiring membrane reprobing (>5 cycles possible)
- Needing long-term archiving
Choose NC when:
- Working with large proteins (>30 kDa)
- Using fluorescence detection
- Operating under budget constraints
Q10: What are the critical steps for successful protein transfer?
A: Essential protocol:
- Membrane preparation
- PVDF: Methanol activation (30 sec)
- NC: Direct equilibration in buffer
- Transfer stack assembly
- Eliminate all air bubbles using roller
- Maintain proper orientation (gel→membrane→filter paper)
- Transfer conditions
- Constant current: 200-300 mA
- Cooling: Ice bath or chilled circulator
- Duration: 1 hr per 1 mm gel thickness
- Post-transfer validation
- Ponceau S staining (reversible)
- Coomassie staining of residual gel (destructive)



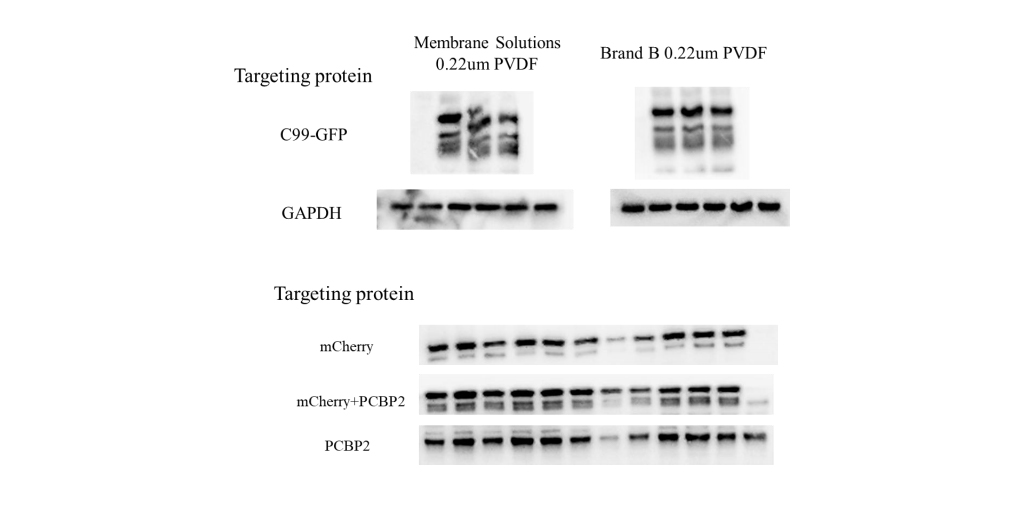


Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *