that there are significant factors contributing to the absence of target watch bands in Western Blot elution buffer. As a matter of fact, it is essential to recognize that the formulation and conditions surrounding elution buffers are critical to achieving precise protein detection. This article provides a comprehensive analysis focusing on how effective elution buffer composition impacts protein analysis and identifies common issues that lead to the absence of target bands. By addressing these factors, we aim to enhance your understanding of the Western Blot protocol and improve overall protein analysis outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Elution buffer composition significantly affects target watch band visibility.
- Understanding protein interactions within the buffer is crucial for detection accuracy.
- Common troubleshooting techniques can mitigate the absence of target bands.
- Optimal conditions in Western Blot protocols enhance protein analysis results.
- Stay informed on best practices for elution buffer formulation.
Introduction to Western Blotting and Elution Buffer
Scientific methodologies often rely on precise techniques for the analysis of proteins. Western blotting stands out as a key method for identifying and quantifying specific proteins within complex mixtures. Several steps in this procedure ensure the effective separation and identification of target proteins, where the choice of elution buffer plays a critical role.
What is Western Blotting?
Western blotting is an analytical method used to detect specific proteins within biological samples. The process comprises protein separation through sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), followed by transferring the proteins onto a membrane. The target proteins are then examined using specific antibodies that bind to them, facilitating detection and quantification.
Importance of Elution Buffer in the Process
The elution buffer is fundamental in the Western Blot protocol. Its primary function is to detach bound proteins from the membrane, making these proteins accessible for subsequent detection steps. The composition of the elution buffer directly influences the efficiency of this release, impacting the clarity and visibility of the target bands crucial for accurate analysis.
Key Components of Typical Elution Buffers
Typical elution buffers contain essential components that enhance protein separation. These include:
- Buffer salts for maintaining pH stability
- pH stabilizers to ensure optimal conditions for protein elution
- Detergents that aid in the solubilization of proteins
- Reducing agents to preserve protein integrity during elution
Understanding the function of each component aids researchers in formulating elution buffers that optimize target protein visibility in Western blotting.
Understanding Target Watch Bands in Western Blot Analysis
The concept of target watch bands plays a significant role in Western blotting techniques, particularly in the analysis of protein detection and identification. Understanding these bands is essential for accurately interpreting experimental results. The presence of distinct protein bands on a membrane indicates successful target identification, directly correlating with the effectiveness of various techniques employed in the procedure.
Definition of Target Watch Bands
Target watch bands are specific bands observed during Western blot analysis that correspond to the proteins of interest. These bands serve as essential indicators of the validation of protein expression levels within a sample. Recognition of these bands is crucial for confirming whether the desired target proteins have been successfully extracted and identified in the presence of the Western Blot elution buffer.
The Role of Specific Proteins in Target Identification
Specific proteins serve as markers that facilitate target identification in Western blotting. Efficient detection of these proteins is heavily dependent on the quality and specificity of the antibodies utilized during the experimental process. Maintaining optimal conditions throughout the experiment enhances the likelihood of achieving clear, discernible target bands that accurately reflect the protein detected.
Common Techniques to Detect Target Bands
Several techniques are essential for detecting target bands effectively. Key practices include:
- Utilizing high-quality antibodies tailored for the specific proteins of interest.
- Optimizing transfer conditions to ensure proteins migrate adequately to the membrane.
- Adjusting the composition of the Western Blot elution buffer for optimal performance.
Implementing these methods can significantly improve the clarity and reliability of target watch bands in Western blot analysis.
Factors Leading to Absence of Target Watch Bands
The absence of target bands in Western blot experiments is often attributed to multiple factors that compromise the accuracy of the detection process. Understanding these underlying issues can help researchers troubleshoot effectively. Significant contributors include binding affinity issues with antibodies, cross-reactivity challenges, and conditions that adversely affect protein stability.
Binding Affinity Issues with Antibodies
Binding affinity serves as a critical indicator of an antibody’s ability to recognize and attach to its specific target protein. In cases where binding affinity is low, the likelihood of obtaining a visible signal reduces significantly, resulting in the potential absence of target bands. This phenomenon can lead to misinterpretation of results and hinder overall assay reliability.
Cross-Reactivity and its Impact on Detection
Cross-reactivity can have a profound impact on the accuracy of detection. When antibodies bind to non-target proteins, they may produce false-positive signals or increase background noise. Optimizing antibody selection and adjusting dilutions are essential steps to mitigate cross-reactivity effects, thereby enhancing the overall clarity of the Western blot results.
Conditions Affecting Protein Stability and Integrity
Protein stability is influenced by environmental conditions such as pH, temperature, and buffer composition. Suboptimal conditions may lead to protein degradation or the loss of critical epitopes necessary for antibody recognition. Ensuring that these factors are maintained at optimal levels is crucial for preserving protein integrity and achieving reliable results in Western blotting.
Key Components of Effective Elution Buffers
The effectiveness of an elution buffer relies heavily on its specific components. Understanding critical aspects such as pH balance, salt concentration, and the role of detergents enables the optimization of protein elution. These factors are essential in ensuring the successful release of proteins during Western blot analysis.
pH Balance and its Importance
The pH balance of elution buffer components plays a significant role in the solubility and stability of proteins. Each protein exhibits unique pH sensitivity, which affects its binding capacity. To enhance elution efficiency, the pH should be adjusted according to the individual characteristics of the proteins being analyzed.
Salt Concentration and Protein Interaction
Salt concentration influences the interaction dynamics between proteins and membranes. Appropriate levels of salt can facilitate stronger binding of proteins to the membrane, ensuring their release during the elution process. Fine-tuning salt concentrations is vital for achieving optimal results in protein recovery.
The Role of Detergents in Elution Buffers
Detergents in buffers, such as Tween-20 or sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), are crucial for minimizing non-specific binding of proteins. This helps improve the clarity of results obtained from Western blotting. It is necessary to optimize the concentration of these detergents according to the specific requirements of each assay to achieve the best outcomes.
| Component | Impact on Elution | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| pH Balance | Affects solubility and binding capacity | Tailor to specific protein characteristics |
| Salt Concentration | Influences protein and membrane interactions | Adjust to enhance binding and elution |
| Detergents in Buffers | Minimizes non-specific binding | Optimize concentration based on assay needs |
The Importance of Protein Loading Controls
In Western Blot analysis, maintaining the accuracy of target detection is essential. One key aspect that significantly contributes to reliable results is the use of protein loading controls. These controls serve as a benchmark for comparing protein levels across different samples, ensuring that variations in target expression are accurately interpreted.
What are Protein Loading Controls?
Protein loading controls refer to reference proteins that are included in gel lanes to standardize loading amounts and validate protein transfer efficiency. By employing common housekeeping proteins, such as actin or GAPDH, researchers can ensure that the variations observed during target detection are not due to inconsistent sample loading.
How Controls Affect Target Detection
Incorporating protein loading controls into Western Blot analysis plays a crucial role in interpreting target detection. These controls confirm equal loading across samples, which aids in determining whether the absence of specific bands arises from technical issues or inherently low protein expression. Without these controls, distinguishing between genuine results and experimental artifacts becomes challenging.
Common Practices for Including Controls
To ensure robust results in Western Blot analysis, it is advisable to follow common practices for including protein loading controls:
- Always utilize a positive control that expresses the target protein to validate detection efficiency.
- Employ a negative control to assess non-specific binding and background noise during the immunoblotting process.
- Regularly check the effectiveness of loading controls to maintain the integrity of the experimental results.
Troubleshooting Absence of Target Bands
When troubleshooting target bands in Western blot analysis, a systematic approach can greatly enhance results. Assessing each component of the experiment helps identify potential issues and improve overall efficiency. This process can involve various factors, including antibody concentrations and gel conditions.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Procedures
Begin with a thorough review of all elements involved in the Western blotting process. This includes checking sample preparation, transfer methods, and gel composition. A precise evaluation at each stage allows for the identification of factors contributing to the absence of target bands.
Adjusting Antibody Concentrations
Antibody concentrations play a crucial role in band detection. Using too high a concentration can lead to saturation, ultimately reducing sensitivity. Conversely, a low concentration might fail to provide the necessary binding for detecting the target. Consider testing a series of dilutions to find the optimal antibody concentration that enhances band visibility.
Optimizing Gel and Transfer Conditions
Ensuring optimal gel and transfer conditions is vital for effective protein migration. Verify gel percentage in conjunction with running and transfer methods. Each of these parameters must be tailored to boost transfer efficiency. Enhancing these elements can significantly improve the visibility of target bands in Western blot analysis.
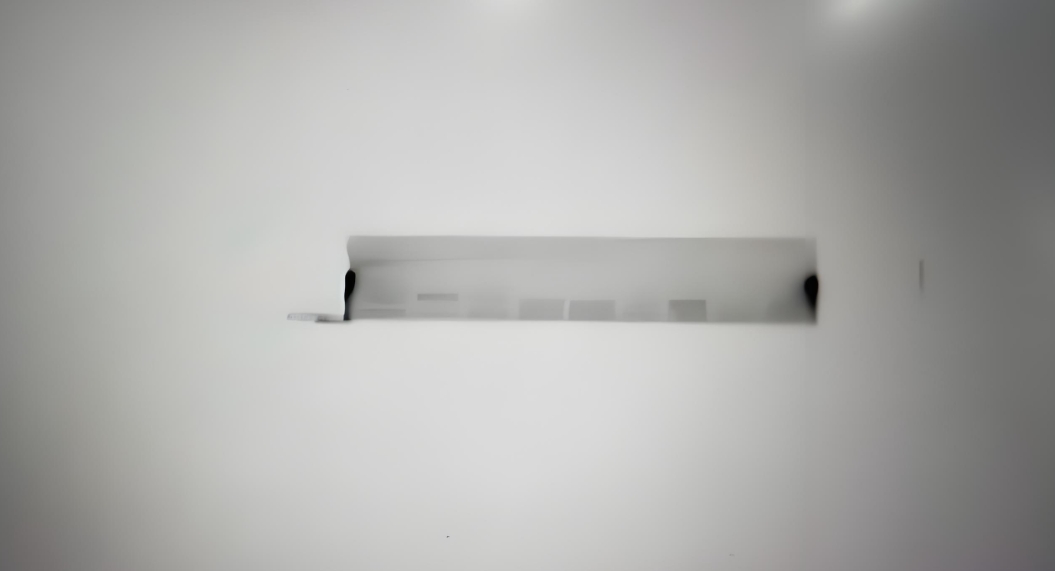

WB experimental bands are not clear
The Role of Gel Concentration in Band Visibility
Understanding the importance of gel concentration is crucial for maximizing band visibility during protein analysis. The choice of gel percentage directly influences the resolution of separated proteins. Selecting an optimal gel based on the molecular weight of your target proteins ensures effective separation and visualization.
How Gel Percentage Affects Resolution
Higher gel concentrations typically provide better resolution for smaller proteins, allowing for distinct band visibility. In contrast, lower concentrations facilitate the separation of larger proteins but may reduce the clarity of smaller bands. Balancing gel concentration is essential for achieving optimal results in Western blotting.
Choosing the Right Gel for Target Proteins
For optimal gel selection, it is vital to consider the molecular weight of the proteins you aim to observe. Pre-cast gels with varying acrylamide percentages cater to different protein sizes, ensuring sharper bands and enhancing detection capabilities. Customizing the gel concentration based on your specific sample requirements yields more effective results.
Impact of Gel Composition on Band Detection
The composition of the gel can significantly affect protein migration patterns. Certain additives may be used to improve visualization and reduce background noise, thereby enhancing overall band visibility. By carefully manipulating gel composition, you can achieve clearer and more defined bands in your analyses.
Analyzing Transfer Efficiency in Western Blotting
Transfer efficiency in Western blotting plays a crucial role in the detection of target proteins. Several factors can significantly affect protein transfer, which may subsequently impact the overall results of experiments. It is vital to understand these factors and implement effective strategies for improvement to enhance transfer outcomes.
Factors Affecting Protein Transfer
Multiple variables contribute to protein transfer efficiency. Key considerations include:
- Type of membrane used: Different membranes have unique binding properties that affect protein retention.
- Electrical parameters: Voltage and current settings during the transfer can influence efficiency and outcome.
- Buffer conditions: The composition and pH of transfer buffers can impact protein mobility and binding interactions.
Strategies to Improve Transfer Results
Enhancing transfer efficiency requires a combination of precise adjustments and best practices. Recommended strategies include:
- Optimization of transfer buffers tailored to specific proteins enhances transfer efficiency.
- Adjusting voltage and transfer time according to the protein size can aid in achieving optimal results.
- Pre-equilibrating the membrane before transfer ensures that binding conditions are optimized.
Assessing Transfer Uniformity
Evaluating the uniformity of protein transfer across lanes is critical for verifying protocol effectiveness. Techniques to assess uniformity include:
- Visual inspections of band quality can provide immediate feedback on transfer results.
- Staining methods, such as Ponceau S, can quantitatively analyze the consistency of protein transfer across the gel.
- Recording results from multiple experiments helps identify patterns or inconsistencies in transfer efficiency.
Importance of Incubation Times and Temperatures
In the realm of Western blotting, creating the right incubation conditions is pivotal for the success of antibody binding. Proper management of these conditions significantly influences the quality of detection and the overall reliability of results.
Optimal Conditions for Antibody Binding
For effective antibody binding optimization, following manufacturer guidelines regarding incubation times and temperatures is crucial. Ensuring these parameters are optimized maximizes signal detection, thereby enhancing the visibility of target proteins during analysis.
How Temperature Influences Protein Integrity
The impact of temperature on proteins cannot be understated. Elevated temperatures often lead to detrimental effects, including protein degradation and aggregation. Lower temperatures typically preserve protein integrity, making them ideal during critical incubation phases. Understanding the temperature effects on proteins assists in gaining reliable assay results.
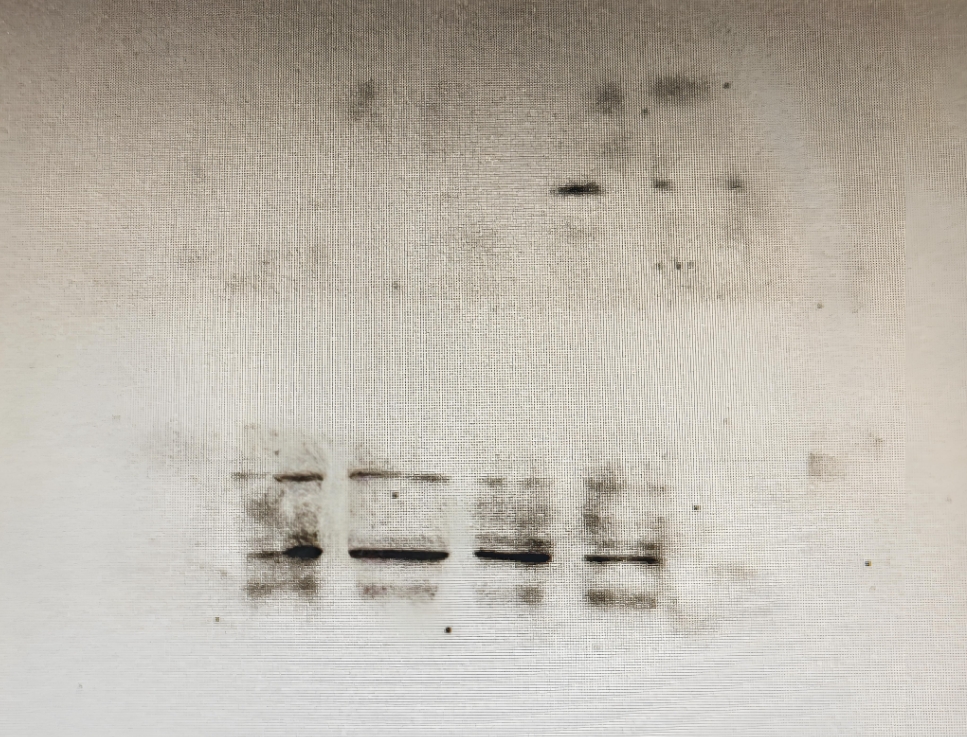
WB experimental bands are not fully displayed
Recommendations for Incubation Protocols
To achieve high specificity in assays, consider extending incubation periods while maintaining lower temperatures. While shorter incubations at high temperatures may generate quick results, they often compromise the quality of the binding. Careful adjustment of incubation times can lead to improved binding efficiency and signal strength.
Case Studies: Successful Troubleshooting of Missing Bands
Exploring effective troubleshooting success stories can enhance our approach to Western blot analysis. The following examples demonstrate how specific adjustments can lead to significant improvements in target band visibility.
Example 1: Adjusting Elution Buffer Components
In one case, a research team reported successful elution buffer adjustments that altered the salt concentration. This minor change resulted in enhanced signal clarity, facilitating the identification of previously missed target bands. Such adjustments can play a crucial role in improving the overall assay performance.
Example 2: Modifying Electrophoresis Conditions
Another study illustrated the impact of electrophoresis modifications. By experimenting with different gel percentages and adjusting the running time, the researchers achieved better resolution for low-abundance proteins. The resulting distinct bands underscored the potential of optimizing these conditions for improved results.
Lessons Learned from Each Case
These case studies highlight the significance of systematic adjustments in Western blotting techniques. They show that even minor tweaks in protocol can yield substantial enhancements in data quality. For further insights into optimizing your procedures, refer to this comprehensive guide on Western blotting technology.
Comparison of Elution Buffer Alternatives
Elution buffer alternatives play a crucial role in optimizing Western blotting processes. Understanding the differences among these buffers can significantly impact your experimental outcomes. Below, we provide insights into common buffer options and considerations for their selection.
Overview of Common Buffer Alternatives
Common elution buffer alternatives include:
- Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS)
- Glycine
- Non-ionic detergents like Triton X-100
Each alternative presents unique benefits depending on your specific experimental requirements.
Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
| Buffer Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| PBS | Widely used, maintains physiological pH | May have limited elution capacity for certain proteins |
| Glycine | Effective for eluting bound proteins | Can cause protein denaturation over time |
| Non-ionic Detergents | Gentle on proteins, suitable for membrane proteins | Potential for high background signaling |
This buffer comparison helps in identifying which elution buffer alternative best suits your needs while considering factors like cost and preparation ease.
When to Consider Switching Buffers
Switching buffers may become necessary if you experience:
- Consistent issues with band clarity
- Excessive background noise
- Failure in detecting target proteins
Enhancing your experiments often requires fresh perspectives on buffer usage. Selecting the appropriate elution buffer can lead to improved signal-to-noise ratios, enabling better visualization of your results.
Conclusion: Ensuring Robust Western Blot Results
In summary, achieving robust Western Blot results necessitates an understanding of the intricate interplay among various experimental factors. Key takeaways include the necessity of utilizing effective antibodies, maintaining controlled experimental conditions, and optimizing buffer formulations. Each of these components must be carefully calibrated to ensure successful protein detection and reproducibility of results.
The field of Western Blotting is poised for significant advancements. Future directions in Western Blot techniques are likely to focus on innovative detection methods aimed at improving sensitivity and specificity. These enhancements will address many prevailing challenges, providing researchers with better tools for protein analysis and identification.
For researchers, it is vital to continuously assess and refine methodologies. Final recommendations stress the importance of adapting to emerging products and protocols while adhering to rigorous experimental designs. By fostering an adaptable approach, you can achieve the most reliable outcomes in protein investigations and contribute to the ongoing evolution of Western Blot practices.
References and further readings:
1.Sousa, M. M. L., Steen, K. W., Hagen, L., & Slupphaug, G. (2011). Antibody cross-linking and target elution protocols significantly modulate signal-to-noise ratio in downstream 2D-PAGE. Proteome Science, 9, 45.
https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/1477-5956-9-45.pdf2.Kurien, B. T., & Scofield, R. H. (2003). Protein blotting: a review. Journal of Immunological Methods, 274(1–2), 1–15.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S00221759020052393.SGilda, J. E., & Bodine, S. C. (2015). Western blotting inaccuracies with unverified antibodies: need for a minimal reporting standard. PLoS One, 10(8), e0135392.
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/file?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0135392&type=printableFAQ
What is the primary function of an elution buffer in Western blotting?
The elution buffer plays a crucial role in releasing bound proteins from the membrane, making them accessible for detection and significantly impacting the efficiency and clarity of the target bands.
Why are target watch bands important in protein analysis?
Target watch bands represent the specific protein bands observed on a membrane that correspond to proteins of interest, essential for validating protein expression levels and ensuring accurate protein detection.
What commonly affects the binding affinity of antibodies in Western blotting?
Factors such as antibody concentration, specificity, and experimental conditions, including pH and temperature, can greatly influence the binding affinity of antibodies to the target protein.
How can the composition of the elution buffer be optimized for better detection?
Optimizing the elution buffer may involve adjusting the salt concentration, pH, and detergent levels to enhance protein elution, reduce background noise, and improve specificity for target detection.
What is the purpose of including protein loading controls in experiments?
Protein loading controls ensure that equal amounts of sample are loaded onto the gel, helping to validate protein transfer efficiency and evaluating whether observed differences in band intensity are due to actual differences in expression or technical issues.
What strategies can be employed to troubleshoot the absence of target bands?
Troubleshooting can include a systematic evaluation of sample preparation, antibody concentrations, gel and transfer conditions, and adjustments to elution buffer components to identify and resolve the underlying issues.
How does gel concentration affect the resolution of protein bands?
Higher gel concentrations provide better resolution for smaller proteins, while lower concentrations are suitable for larger proteins, ensuring effective size-based separation during electrophoresis.
What factors can influence the transfer efficiency during Western blotting?
Key factors include the type of membrane used, the applied voltage during transfer, buffer conditions, and equilibration of the membrane prior to the transfer, all of which can significantly impact the quality of protein transfer.
What role do incubation conditions play in protein detection?
Optimal incubation conditions, including temperature and time, are vital for maximizing the binding of antibodies to the target protein, thus enhancing signal detection and overall assay performance.
When should researchers consider switching their elution buffer?
Researchers should consider switching elution buffers if they consistently encounter issues with band clarity, excessive background noise, or failed target detection, aiming for an improved signal-to-noise ratio.
Leo Bios
Hello, I’m Leo Bios. As an assistant lecturer, I teach cellular and
molecular biology to undergraduates at a regional US Midwest university. I started as a research tech in
a biotech startup over a decade ago, working on molecular diagnostic tools. This practical experience
fuels my teaching and writing, keeping me engaged in biology’s evolution.




Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *