This method includes steps like separating proteins, transferring them, and detecting them. It gives researchers important information about specific proteins in mixtures.
In this article, we will explain the immunoblot technique. We will talk about the importance of molecular weight markers. We will also cover how to measure protein size accurately. By the end, you’ll know how to use immunoblotting for protein analysis in your work.
Key Takeaways
- Immunoblotting is vital for accurate protein size determination.
- Protein size measurement aids in understanding protein function and expression.
- Molecular weight markers are essential for size comparison in Western blots.
- Choosing the right detection techniques enhances the reliability of results.
- Understanding gel electrophoresis improves interpretation of protein sizes.
- Addressing common issues can significantly enhance experimental outcomes.
Understanding the Immunoblot Technique
Immunoblotting, also known as the immunoblot technique, is a key method for finding specific proteins in samples. It helps researchers study proteins in detail.
What is Immunoblotting?
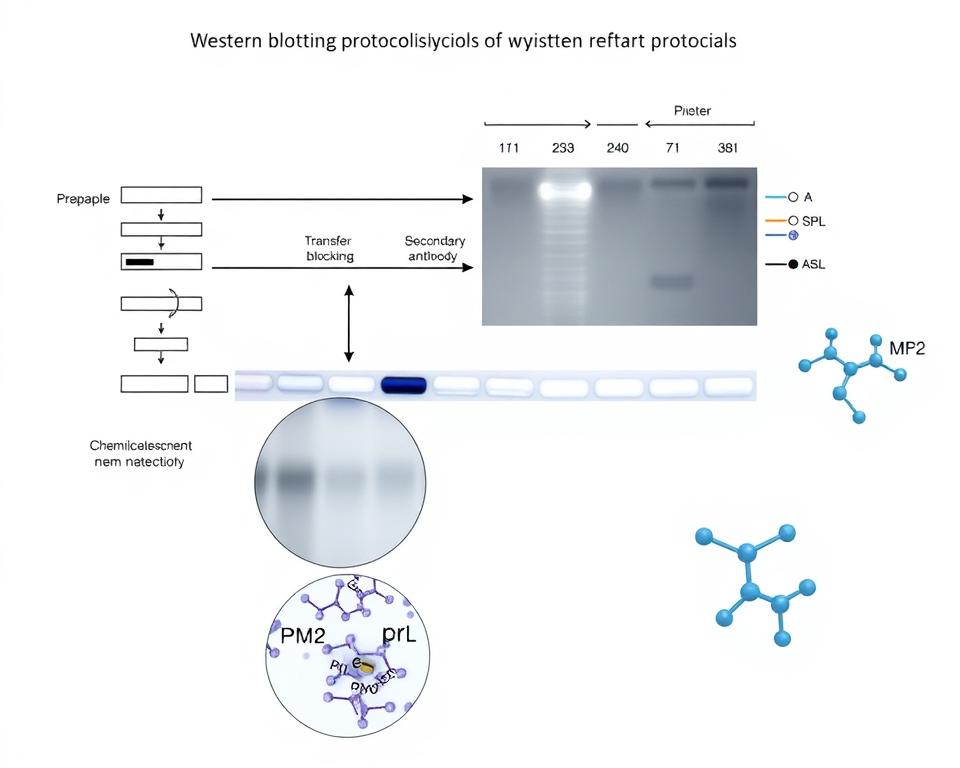
The immunoblotting process has several important steps. First, proteins are sorted by molecular weight using SDS-PAGE. Then, they are transferred to a membrane, like nitrocellulose or PVDF.
This membrane is tested with specific antibodies. These antibodies find and bind to the target proteins. This makes it possible to detect them.
Key Components of the Immunoblot Process
To understand immunoblotting, you need to know its main parts:
- Separation of Proteins: Proteins are sorted by molecular weight using SDS-PAGE.
- Transfer to Membrane: Proteins are moved to a membrane for analysis.
- Antibody Probing: Specific antibodies find and bind to the proteins.
Common Applications in Research
The immunoblot technique is crucial in many research areas, such as:
- Studying how much protein is present.
- Looking at protein changes after they are made.
- Examining how proteins interact with each other.
Its wide use makes immunoblotting a key tool for scientists. They use it to understand protein functions and how they are controlled.
The Role of Molecular Weight Markers
Molecular weight markers are key in protein size determination. They are known as protein ladders. These markers have known molecular weights. They help researchers compare protein sizes in samples accurately.
What are Molecular Weight Markers?
Molecular weight markers are protein preparations used in gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. They help estimate protein molecular weights. By comparing them to target proteins, researchers can get precise molecular weight estimates.
How to Choose the Right Marker for Your Experiment
Choosing the right molecular weight marker is crucial. Consider the following:
- Range of Molecular Weights: Make sure the marker covers your target proteins’ molecular weights.
- Validation: Pick markers validated for your detection method, like chemiluminescent or fluorescent systems.
- Concentration and Volume: Choose a marker concentration that’s visible and accurate for size determination.
The right molecular weight marker leads to reliable size determination in immunoblotting. This boosts confidence in research results.
| Marker Name | Molecular Weight Range (kDa) | Detection Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| SeeBlue Plus2 | 3.5 – 250 | Chemiluminescent | Good for a broad range of proteins |
| Broad Range Protein Ladder | 10 – 250 | Fluorescent | High sensitivity and visibility |
| Precision Plus Protein Standards | 10 – 250 | Chemiluminescent | Includes a colorimetric standard for ease of use |
Gel Electrophoresis and Its Importance
Gel electrophoresis is key in molecular biology and biochemistry. It helps separate proteins by size. This lets researchers study protein mixtures well. Knowing the different types of gel electrophoresis can greatly improve results.
Types of Gel Electrophoresis
There are many types of gel electrophoresis, each for different needs:
- SDS-PAGE: This method uses SDS to break down proteins. It separates them by size. It’s great for checking protein purity and size.
- Native PAGE: This keeps proteins as they are. It separates them by size and charge. It’s good for studying how proteins work together.
How Gel Composition Affects Result Interpretation
The type of gel used is very important. The amount of acrylamide in the gel changes its pore size:
| Acrylamide Concentration | Pore Size | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Low (2-7%) | Large | Larger proteins |
| Medium (8-12%) | Medium | Proteins of average size |
| High (12-20%) | Small | Smaller proteins |
Choosing the right gel composition is crucial. The wrong choice can make it hard to understand protein sizes and functions.
Transferring Proteins to Membranes
Transferring proteins to membranes is a key step in the immunoblot technique. It helps researchers analyze proteins after gel electrophoresis. Different methods are used to transfer proteins efficiently, affecting the technique’s success.
Mechanisms of Protein Transfer
The main ways to transfer proteins include:
- Wet Transfer: This method uses a lot of buffer and takes longer. It’s very efficient.
- Semi-Dry Transfer: It needs less buffer and is faster. But, it’s harder for big proteins.
- Fast Transfer: It saves time but might not work well for big proteins.
Factors Affecting Transfer Efficiency
Several things can change how well proteins transfer:
- Buffer Composition: Adding methanol to the buffer helps protein binding. But, it might lower yields for big proteins.
- Membrane Condition: The type of membrane used affects how well proteins bind. This impacts success.
Knowing these factors helps improve protein transfer to membranes. This makes your immunoblot results stronger.
Antibody Selection for Immunoblotting
Choosing the right antibodies is key to successful immunoblotting. This step involves picking primary and secondary antibodies. They must effectively find and stick to the target protein, leading to accurate results.
Types of Antibodies Used
There are two main types of antibodies in immunoblotting:
- Primary Antibodies: These antibodies specifically target the proteins of interest, facilitating their identification and quantification.
- Secondary Antibodies: Conjugated to detection molecules, secondary antibodies amplify the signal, enhancing the overall visibility of the detected proteins.
Importance of Specificity and Sensitivity
Specificity and sensitivity are crucial for accurate results in immunoblotting. Specificity means the antibodies only bind to the right protein, reducing background noise. This is important for telling apart similar proteins.
Sensitivity is about finding proteins that are present in small amounts. This is key in finding disease markers. Using well-tested antibodies makes immunoblot results more reliable. It helps in drawing solid conclusions from the data.

Detection Techniques for Protein Quantification
Protein quantification uses different detection methods. Each method has its own benefits and drawbacks. It’s important to pick the right one for accurate results in immunoblotting.
Common Detection Methods
There are mainly two detection techniques: chemiluminescence and colorimetric methods. Both are key for measuring proteins in samples.
- Chemiluminescence: This method uses light from a chemical reaction. It’s very sensitive and great for finding small amounts of proteins. It’s often the top choice for detailed analysis.
- Colorimetric Techniques: These methods change color based on protein levels. They’re not as sensitive as chemiluminescence but are simpler and faster to use.
Comparing Chemiluminescence and Colorimetric Techniques
When we compare these methods, several things matter:
| Characteristic | Chemiluminescence | Colorimetric Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | High | Moderate |
| Detection Time | Rapid | Quick |
| Equipment Requirements | Advanced imaging systems required | Standard lab equipment sufficient |
In short, each method has its own advantages and uses. The choice depends on what the research needs for protein measurement.
Analyzing Band Size and Intensity
Getting the right band size and intensity is key in immunoblot protein sizing. It helps figure out the molecular weight of proteins and how much is in a sample. This way, researchers can understand how proteins are expressed.
Techniques for Size Measurement
There are many ways to measure protein size on immunoblots:
- Densitometry: This method uses software to measure the intensity of bands. It helps compare different samples.
- Standard Curves: Making standard curves with known proteins helps measure unknown sizes accurately.
Quantitative Analysis of Band Intensity
Looking at band intensity tells us about protein amounts. Combining size and intensity analysis makes results more reliable. This way, researchers can really see how proteins are expressed under different conditions.
Factors Influencing Protein Size Assessment
In protein analysis, several factors can change how we measure protein size. Post-translational modifications and protein conformation are key. They affect how proteins move and are sized during immunoblotting. Knowing these factors is crucial for precise research analysis.
Post-Translational Modifications
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are changes proteins go through after they’re made. These changes can alter a protein’s size and charge. This affects how it moves in electrophoresis. Common PTMs include:
- Phosphorylation
- Glycosylation
- Ubiquitination
- Methylation
Each PTM adds unique traits that make sizing and function analysis tricky. This size variation means we must be precise in our analysis.
Protein Conformation and Size Variability
Protein conformation is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. This shape influences how proteins move through a gel. Misshapen or changed proteins might move differently than normal ones. This can cause wrong size guesses. Factors that change protein conformation include:
- Environmental conditions (pH, temperature)
- Interactions with other biomolecules
- Conformational stability
These differences show why we must think about protein shape when sizing in immunoblotting.
| Factor | Impact on Protein Size Assessment |
|---|---|
| Post-Translational Modifications | Alter size and charge; complicate migration behavior |
| Protein Conformation | Affects migration patterns during electrophoresis |
Troubleshooting Common Immunoblot Issues
Fixing problems with immunoblotting is key to getting accurate results. Issues like specificity problems, band smearing, and background noise are common. Knowing what causes these problems and how to fix them is important.
Addressing Specificity Problems
Specificity issues often show up as high background signals. This means the antibodies are binding to things they shouldn’t. Using high-quality antibodies is a big step towards solving this. Also, making sure the blocking conditions are right can help a lot.
Looking for reliable antibody selection guidelines can be very helpful. For more tips on improving specificity, check out this resource.
Resolving Band Smearing and Background Noise
Band smearing can happen if you’re not careful with the gel or how you load the samples. Making sure all samples are loaded equally is important. Also, getting the transfer parameters just right can help avoid smearing.
These steps will make your immunoblot clearer. Knowing what causes background noise helps you fix it too.
Case Studies: Protein Size Determination in Specific Research
Case studies show how immunoblotting is used in different fields. This includes cancer research and neurobiology studies. They highlight the importance of knowing protein sizes to understand important biological processes.
Example 1: Cancer Research
In cancer research, immunoblotting is key for finding specific tumor markers. Knowing protein sizes helps researchers understand how cancer grows. Studies have found new biomarkers that help predict how well patients will do with certain treatments.
This is important for personalized medicine. It means doctors can give treatments that fit each patient’s needs, based on their protein profiles.
Example 2: Neurobiology Studies
Neurobiology studies use immunoblotting to look at proteins in neurons. By finding out the sizes of these proteins, researchers learn about brain function and diseases. This knowledge helps them understand how the brain works and could lead to new treatments.
| Research Field | Application of Immunoblotting | Significance of Protein Size Determination |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer Research | Identification of tumor markers | Facilitates personalized medicine development |
| Neurobiology Studies | Analysis of protein expression in neurons | Insights into neurological conditions |
Future Trends in Protein Size Analysis
Looking ahead, protein size analysis is set for big changes. New detection technologies are making things more sensitive and quick. This means researchers can get results faster and more accurately, which is key in fast-paced science.
New methods like multiplex immunoblotting are also changing the game. They let scientists check many things at once. This gives a full picture of how proteins change in different samples. It’s an exciting time for those studying proteins.
To stay ahead, scientists need to keep up with these new trends. Using the latest in detection and techniques will make their work better. This progress will help us understand proteins and their roles in many areas of research.
References and further readings:
1.Kurien, B. T., & Scofield, R. H. (2006). Western blotting. Methods, 38(4), 283–293.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1046202306000065?via%3Dihub
2.Mahmood, T., & Yang, P. C. (2012). Western blot: Technique, theory, and trouble shooting. North American Journal of Medical Sciences, 4(9), 429–434.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3509629/
3.Renart, J., Reiser, J., & Stark, G. R. (1979). Transfer of proteins from gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection with antisera: A method for detecting antibodies in sera. PNAS, 76(7), 3116–3120.
FAQ
How can protein size be determined from an immunoblot?
To find out a protein’s size, first separate it using SDS-PAGE. Then, transfer it to a membrane. Use specific antibodies to probe it. By comparing the bands with markers, you can estimate the size accurately.
What is the significance of molecular weight markers in immunoblotting?
Molecular weight markers help estimate protein sizes. They are crucial for accurate analysis. Choosing the right marker is key for reliable results.
How does gel composition influence the results of protein size determination?
The gel’s composition, especially the acrylamide, affects protein separation. Higher acrylamide is better for small proteins. Lower acrylamide works for larger proteins. This impacts the accuracy of immunoblot analysis.
What factors can affect protein transfer efficiency during immunoblotting?
Transfer efficiency is influenced by the buffer’s composition, the membrane’s condition, and the transfer method. Methanol in the buffer helps protein binding but might reduce larger protein yields.
Why is antibody specificity important in immunoblotting?
Specific antibodies ensure only the target protein binds. This reduces background signals, crucial for accurate detection and quantification in immunoblot analysis.
What are some common detection methods used in protein quantification?
Chemiluminescence is highly sensitive, while colorimetric techniques show color changes that reflect protein amounts. The choice depends on the experiment’s needs.
How can band size and intensity be analyzed in an immunoblot?
Analyze band size and intensity with densitometry for intensity quantification. Use standard curves with known concentrations for comparative analysis of unknown samples.
What challenges can arise during protein size assessment, and how can they be addressed?
Post-translational modifications and conformation issues can affect size and migration. To overcome these, control conditions, optimize antibody usage, and refine transfer protocols.
Can you provide examples of practical applications of immunoblotting in research?
Immunoblotting is key in cancer research for identifying markers. It’s also used in neurobiology to study protein expressions related to neuronal function and pathology. It’s versatile in biological research.
What emerging trends are shaping protein size analysis?
Trends include better detection technologies and multiplex immunoblotting. These advancements enhance protein profiling capabilities by analyzing multiple targets at once.
Leo Bios
Hello, I’m Leo Bios. As an assistant lecturer, I teach cellular and
molecular biology to undergraduates at a regional US Midwest university. I started as a research tech in
a biotech startup over a decade ago, working on molecular diagnostic tools. This practical experience
fuels my teaching and writing, keeping me engaged in biology’s evolution.





Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *